Telescopes Keck I and Keck II
Mauna Kea Access Road, Mauna Kea,, Hawai (HI 96720)
United States
The Maunakea Observatories Complex is a group of world-class telescopes located near the summit of Maunakea volcano in Hawaii. Thanks to its ideal conditions for astronomy, it hosts facilities from various countries and is one of the most important observation centers in the world.
Descripción
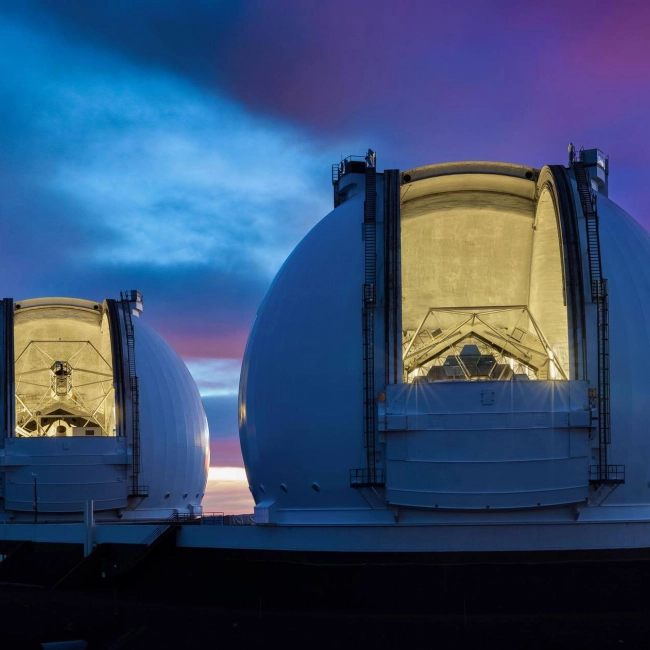
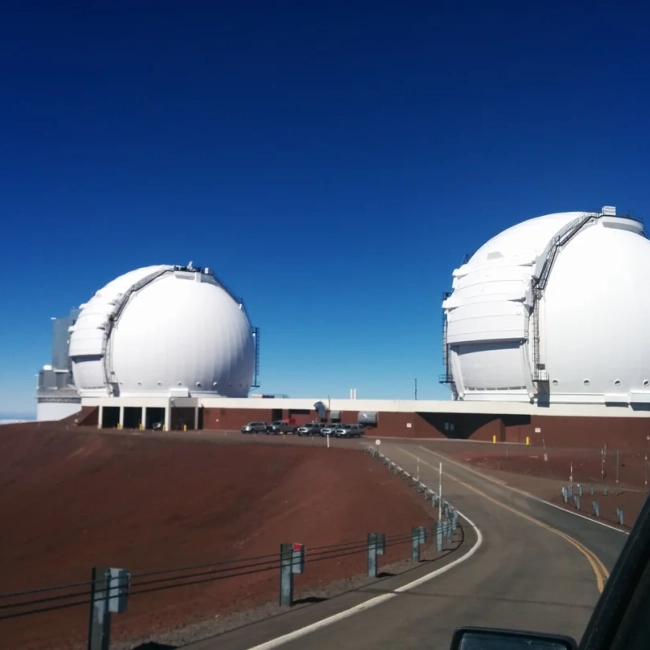
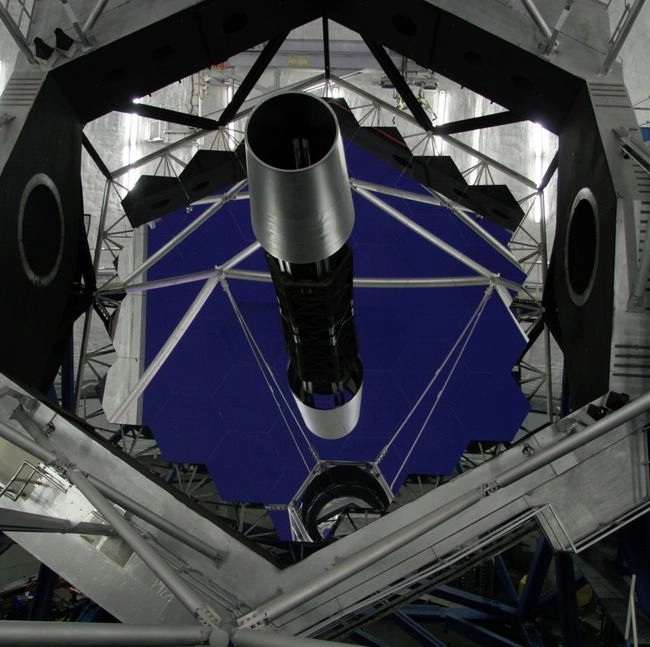
The Keck I and Keck II telescopes are two of the most powerful astronomical instruments in the world. They are located at the W. M. Keck Observatory on top of the dormant Mauna Kea volcano in Hawaii, at an altitude of over 4,200 meters. This site is one of the best in the world for astronomical observations, thanks to its stable atmosphere, minimal light pollution, and dry air.
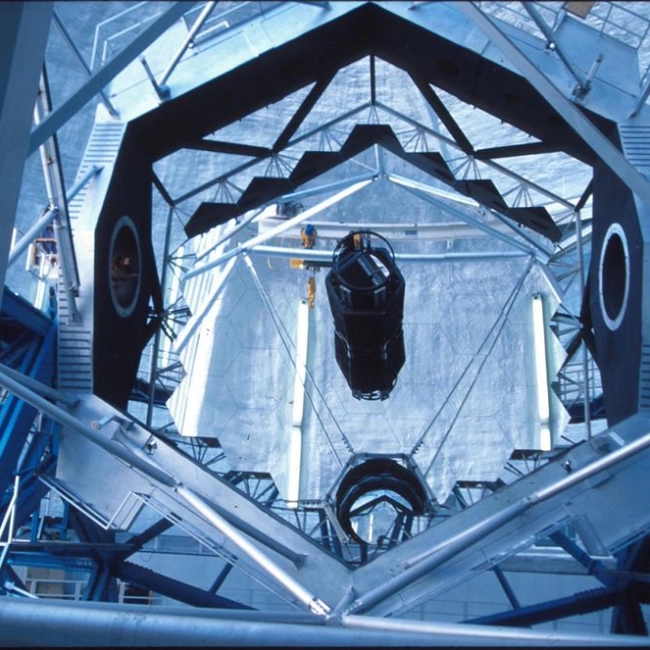
Both telescopes are reflecting telescopes of the modified Cassegrain design, each featuring a 10-meter primary mirror. Unlike traditional single-piece mirrors, these mirrors are made up of 36 hexagonal segments, which are controlled by an active system that keeps them perfectly aligned. This innovative design allows them to gather vast amounts of light with exceptional precision.
Keck I began operations in 1993, and Keck II followed in 1996. Together, they have been instrumental in numerous discoveries in modern astronomy. They have been used to study exoplanets, distant galaxies, supernovae, and the orbits of stars near the center of the Milky Way, helping to confirm the existence of a supermassive black hole.
Both telescopes are equipped with advanced adaptive optics systems, which correct atmospheric distortions in real time. This allows them to capture images as clear as if they were taken in space. Thanks to these capabilities, the Keck telescopes remain a global benchmark for astronomical research.
Datos técnicos del telescopio
- Optical System Type: Maksutov-Cassegrain Telescope
- Mount Type: Equatorial Mount
- Mount Movement Type: Computerized Mount